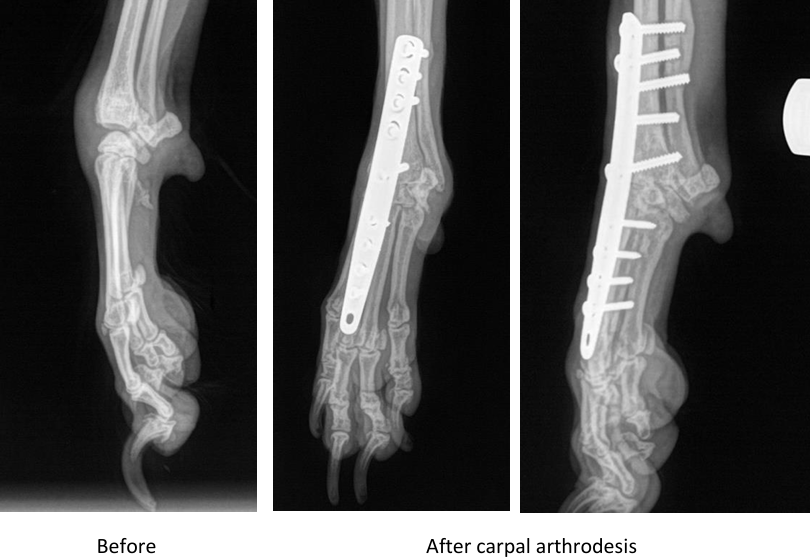
Joint fusion (arthrodesis)
Arthrodesis is a surgical procedure stabilizing a joint by fusing the bones across the joint.
The surgery involves removing the joint cartilage and using surgical implants to compress and stabilize the joint. This allows the bones on either side of the joint to fuse together, eliminating movement and providing stability. The most commonly used surgical implants are plates and screws. However, other techniques may be used as well.
Why is arthrodesis performed?
Treatment of severe osteoarthritis is the most common reason to perform an arthrodesis. Arthrodesis can also be performed to repair complex bony fractures that extend into the joint or to stabilize a joint that has sustained injury to the supporting soft tissue structures (torn ligaments or tendons).